数据结构算法复杂度
1、影响算法效率的主要因素
(1)算法采用的策略和方法;
(2)问题的输入规模;
(3)编译器所产生的代码;
(4)计算机执行速度。
2、时间复杂度
// 时间复杂度:2n + 5 long sum1(int n) { long ret = 0; 1 int* array = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); 1 int i = 0; 1 for(i=0; i<n; i++) n { array[i] = i + 1; } for(i=0; i<n; i++) n { ret += array[i]; } free(array); 1 return ret; 1 } 时间复杂度: n + 3 long sum2(int n) { long ret = 0; 1 int i = 0; 1 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) n { ret += i; } return ret; 1 } 时间复杂度: 3 long sum3(int n) { long ret = 0; 1 if( n > 0 ) { ret = (1 + n) * n / 2; 1 } return ret; 1 }
随着问题规模n的增大,它们操作数量的差异会越来越大,因此实际算法在时间效率上的差异也会变得非常明显!
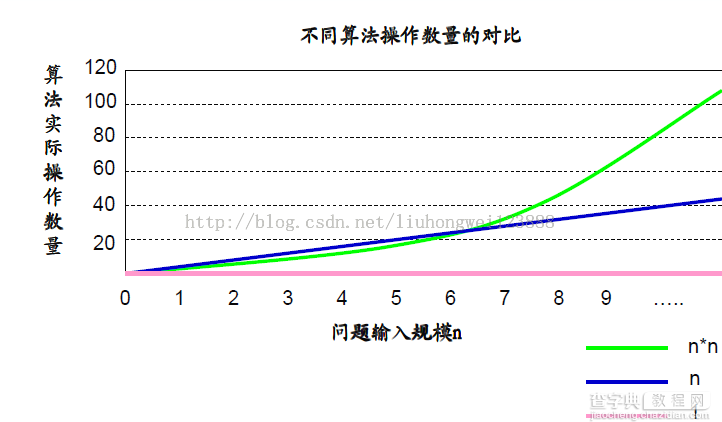
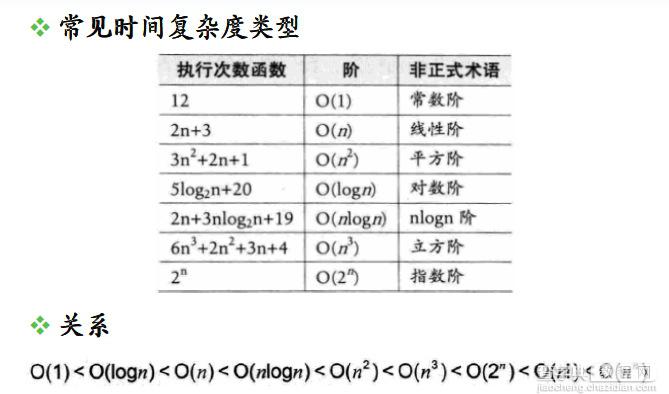
判断一个算法的效率时,往往只需要关注操作数量的最高次项,其它次要项和常数项可以忽略。

在没有特殊说明时,我们所分析的算法的时间复杂度都是指最坏时间复杂度。
3、空间复杂度
//空间复杂度:12 + n long sum1(int n) { long ret = 0; 4 int* array = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); 4 + 4 * n int i = 0; 4 for(i=0; i<n; i++) { array[i] = i + 1; } for(i=0; i<n; i++) { ret += array[i]; } free(array); return ret; } 空间复杂度: 8 long sum2(int n) { long ret = 0; 4 int i = 0; 4 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { ret += i; } return ret; } 空间复杂度: 4 long sum3(int n) { long ret = 0; 4 if( n > 0 ) { ret = (1 + n) * n / 2; } return ret; }
多数情况下,算法执行时所用的时间更令人关注,如果有必要,可以通过增加空间复杂度来降低时间复杂度,同理,也可以通过增加时间复杂度来降低空间复杂度,具体问题,具体分析。
数据结构顺序表
表是具有相同类型的n(n >= 0)个数据元素的有限序列,即:
线性表(List)是零个或多个数据元素的集合 线性表中的数据元素之间是有顺序的 线性表中的数据元素个数是有限的 线性表中的数据元素的类型必须相同
//seq_list.h #ifndef _SEQ_LIST_H_ #define _SEQ_LIST_H_ struct seq_list { int capacity; int length; unsigned int *node; }; struct seq_list* seq_list_create(int capacity); int seq_list_capacity(struct seq_list* list); int seq_list_length(struct seq_list* list); int seq_list_insert(struct seq_list* list, int position, void* data); void* seq_list_get(struct seq_list* list, int position); void* seq_list_remove(struct seq_list* list, int position); void seq_list_clear(); void seq_list_destroy(struct seq_list* list); #endif //seq_list.c #include "seq_list.h" #include <stddef.h> #include <malloc.h> struct seq_list* seq_list_create(int capacity) { int i = 0; struct seq_list* ret = NULL; if (capacity >= 0) { ret = (struct seq_list*) malloc(sizeof(struct seq_list) + sizeof(unsigned int) * capacity); if (ret != NULL) { ret->capacity = capacity; ret->length = 0; ret->node = (unsigned int*) (ret + 1); } } return ret; } int seq_list_insert(struct seq_list* list, int position, void* data) { int i = 0; int ret; ret = (list != NULL); ret = ret && position >= 0 && position < list->capacity; ret = ret && list->length < list->capacity; if (ret) { for (i = list->length; i > position; i--) { list->node[i] = (list->node[i - 1]); } list->node[i] = (unsigned int)data; double *p = (double *)data; list->length++; } return ret; } void* seq_list_get(struct seq_list* list, int position) { void* ret = NULL; if (list != NULL && position >= 0 && position < list->length) { ret = (void *)list->node[position]; } return ret; } void* seq_list_remove(struct seq_list* list, int position) { void* ret = NULL; int i = 0; if (list != NULL && position >= 0 && position < list->length) { int i = 0; ret = seq_list_get(list, position); for (i = position + 1; i < list->length; i++) { list->node[i - 1] = list->node[i]; } list->length--; } return ret; } int seq_list_capacity(struct seq_list* list) { int ret = -1; if (list != NULL) { ret = list->capacity; } return ret; } int seq_list_length(struct seq_list* list) { int ret = -1; if (list != NULL) { ret = list->length; } return ret; } void seq_list_clear(struct seq_list* list) { if (list != NULL) { list->length = 0; } } void seq_list_destroy(struct seq_list* list) { free(list); list = NULL; } //seq_list_main.c #include <stdio.h> #include "seq_list.h" int main(void) { struct seq_list* list = seq_list_create(100); double *p = NULL; int ret = 0; double a = 1.1; double b = 2.2; double c = 3.3; double d = 4.4; double e = 5.5; seq_list_insert(list, 0, &a); seq_list_insert(list, 1, &b); seq_list_insert(list, 2, &c); seq_list_insert(list, 3, &d); seq_list_insert(list, 4, &e); printf("list capacity = %d, length = %dn", seq_list_capacity(list), seq_list_length(list)); p = (double *)seq_list_get(list, 0); if (p != NULL) { printf("%lfn", *p); } p = (double *)seq_list_get(list, 3); if (p != NULL) { printf("%lfn", *p); } p = (double *)seq_list_remove(list, 3); if (p != NULL) { printf("remove data %lf, index at 3 , after length: %dn", *p, seq_list_length(list)); } p = (double *)seq_list_get(list, 3); if (p != NULL) { printf("after remove, index at 3: %lfn", *p); } seq_list_clear(list); printf("after clear, list length is %dn", seq_list_length(list)); seq_list_destroy(list); return 0; }
【用C语言举例讲解数据结构中的算法复杂度结与顺序表】相关文章:
★ 浅析C语言中printf(),sprintf(),scanf(),sscanf()的用法和区别
