在android中提供了常见的几种ViewGroup的实现,包括LinearLayout、Relativeayout、FrameLayout等。这些ViewGroup可以满足我们一般的开发需求,但是对于界面要求复杂的,这几个布局就显得捉襟见肘了。所以自定义的ViewGroup在我们接触过的应用中比比皆是。
要想实现一个自定义的ViewGroup,第一步是学会自定义属性,这些自定义的属性将让我们配置布局文件的时候更加的灵活。自定义属性是在value目录下声明一个attrs.xml文件。
<"1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="CascadeViewGroup"> <attr name="verticalspacing" format="dimension"/> <attr name="horizontalspacing" format="dimension"/> </declare-styleable> <declare-styleable name="CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams"> <attr name="layout_paddingleft" format="dimension"/> <attr name="layout_paddinTop" format="dimension"/> </declare-styleable> </resources>
在这里我们声明了两个自定义属性集,CascadeViewGroup中的属性是针对我们自定义的CascadeViewGroup组件设置的,也就是可以在布局文件中<CascadeViewGroup>标签中可以使用的属性。另外一个CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams则是针对于CascadeViewGroup中的子View设置的属性。
在编写代码前,我们还设置了一个默认的宽度和高度供CascadeLayout使用。这两个属性在dimens.xml定义。
<"1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <dimen name="default_horizontal_spacing">10dp</dimen> <dimen name="default_vertical_spacing">10dp</dimen> </resources>
下面开始编写自定义的组件CascadeLayout了。
package com.app.CustomViewMotion; import android.content.Context; import android.content.res.TypedArray; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; /** * Created by charles on 2015/8/13. */ public class CascadeViewGroup extends ViewGroup { //自定义布局中设置的宽度和高度 private int mHoriztonalSpacing; private int mVerticalSpacing; public CascadeViewGroup(Context context) { this(context, null); } public CascadeViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public CascadeViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) { super(context, attrs, defStyle); TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup); try { //获取设置的宽度 mHoriztonalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_horizontalspacing, this.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.default_horizontal_spacing)); //获取设置的高度 mVerticalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_verticalspacing, this.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.default_vertical_spacing)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { a.recycle(); } } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { final int count = this.getChildCount(); int width = this.getPaddingLeft(); int height = this.getPaddingTop(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View currentView = this.getChildAt(i); this.measureChild(currentView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = (CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams) currentView.getLayoutParams(); if(lp.mSettingPaddingLeft != 0){ width +=lp.mSettingPaddingLeft; } if(lp.mSettingPaddingTop != 0){ height +=lp.mSettingPaddingTop; } lp.x = width; lp.y = height; width += mHoriztonalSpacing; height += mVerticalSpacing; } width +=getChildAt(this.getChildCount() - 1).getMeasuredWidth() + this.getPaddingRight(); height += getChildAt(this.getChildCount() - 1).getMeasuredHeight() + this.getPaddingBottom(); this.setMeasuredDimension(resolveSize(width, widthMeasureSpec), resolveSize(height, heightMeasureSpec)); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean b, int l, int i1, int i2, int i3) { final int count = this.getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View currentView = this.getChildAt(i); CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = (CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams) currentView.getLayoutParams(); currentView.layout(lp.x, lp.y, lp.x + currentView.getMeasuredWidth(), lp.y + currentView.getMeasuredHeight()); } } public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams { int x; int y; int mSettingPaddingLeft; int mSettingPaddingTop; public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) { super(c, attrs); TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams); mSettingPaddingLeft = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams_layout_paddingleft, 0); mSettingPaddingTop = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams_layout_paddinTop, 0); a.recycle(); } public LayoutParams(int width, int height) { super(width, height); } public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) { super(source); } } @Override protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() { return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); } @Override protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) { return new LayoutParams(p); } @Override public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) { return new LayoutParams(this.getContext(), attrs); } }
代码稍微优点长,但是结构还是很清晰的。
1)构造方法中或者XML文件中配置属性的值。通过TypedArray中的方法获取我们在layout布局中设置的属性,并且将他们保存在成员变量中。
2)构造自定义的内部类LayoutParams。构造这个内部类,可以方便我们在测量我们的子View的时候保存他们的属性值,以便在Layout阶段布局。
3)generateLayoutParams()、generateDefaultParams()等方法。在这些方法中返回我们自定义的layoutParams。至于为什么要重写这些方法,可以查看ViewGroup类的addView()方法就很清楚了。
4)measure阶段。在measure阶段,我们会测量自己的大小,同时也要测量子View的大小,并且将子View的信息保存在LayoutParams中。
5)layout阶段。根据各个子View的信息,布局他们的位置。
最后加上布局文件。
<"1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <> <> <com.app.CustomViewMotion.CascadeViewGroup xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:ts="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.app.CustomViewMotion" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" ts:horizontalspacing="15dp" ts:verticalspacing="15dp"> <TextView android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="text1" android:background="#668B8B"/> <TextView android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="text2" android:background="#FFDAB9"/> <TextView android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="text3" android:background="#43CD80"/> <> <TextView android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="text4" ts:layout_paddingleft="100dp" ts:layout_paddinTop="100dp" android:background="#00CED1"/> </com.app.CustomViewMotion.CascadeViewGroup>
实现的效果如下:
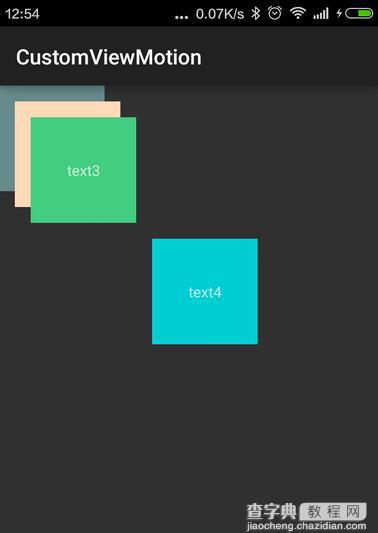
以上就是的全部内容,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持查字典教程网。
【Android自定义ViewGroup的实现方法】相关文章:
★ android TextView设置中文字体加粗实现方法
★ Android定制RadioButton样式三种实现方法
★ android中ListView多次刷新重复执行getView的解决方法
