先看下最终的效果
开始实现
新建一个ClockView集成View
public class ClockView extends View { }
先重写onMeasure方法,这里要先说一下View的测量模式,一共有三种:
1、EXACTLY
即精确值模式,当我们将控件的layout_width属性或layout_height属性指定为具体数值时,比如android:layout_width="100dp",或者指定为math_parent属性时(占据父View的大小),系统使用的是EXACTLY模式。
2、AT_MOST
即最大值模式,当控件的layout_width属性或layout_height属性指定为wrap_content时,控件大小一般随着控件的子控件或内容的变化而变化,此时控件的尺寸只要不超过父控件允许的最大尺寸即可。
3、UNSPECIFIED
这个属性比较奇怪——它不指定其大小测量模式,View想多大就多大,通常情况下在绘制自定义View时才会使用。
因为View的onMeasure方法只支持EXACTLY模式,当layout_width和layout_height为wrap_content时,View的大小就显得很奇怪了,如下图。
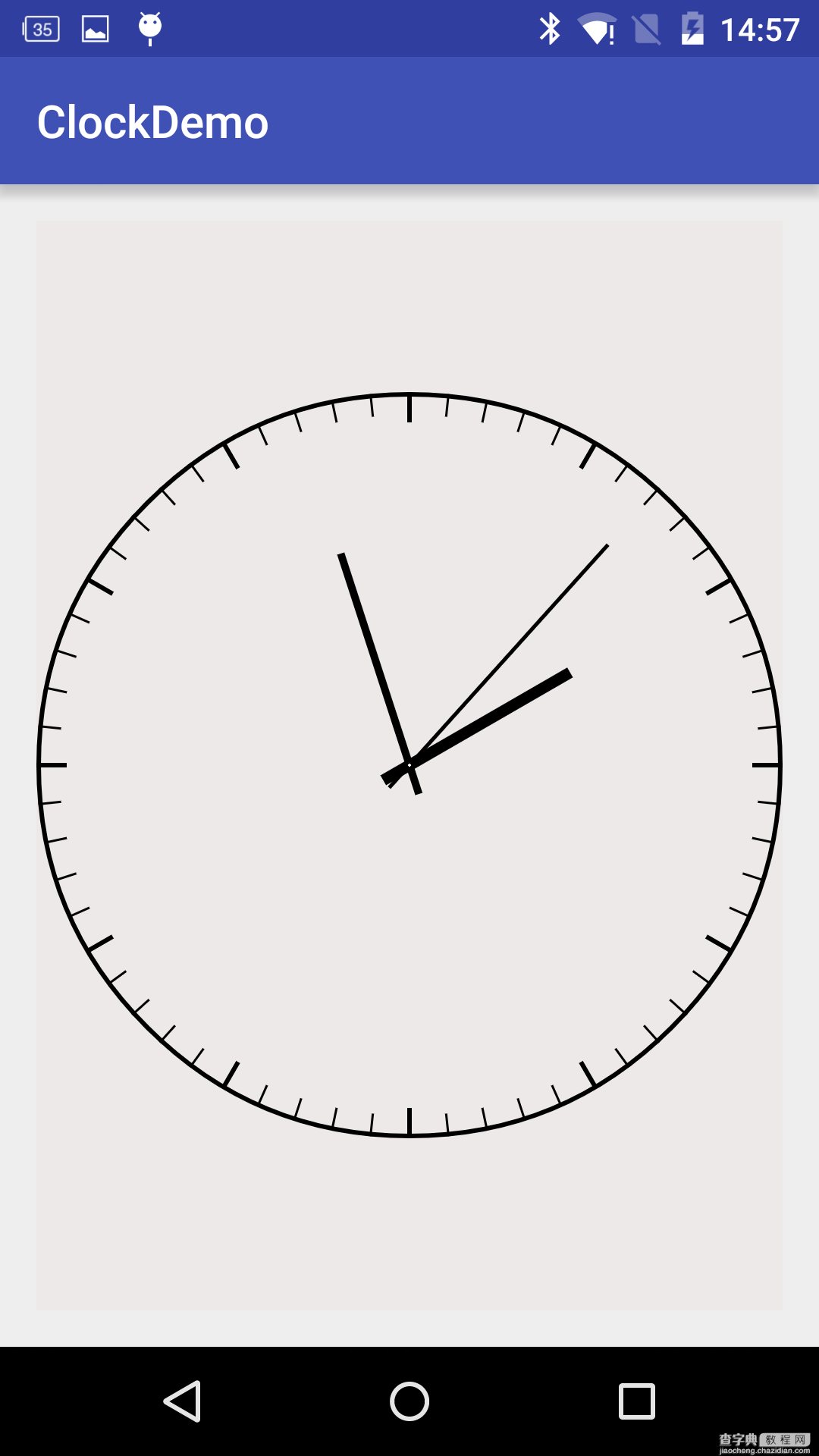

所以我们重写一下onMeasure方法可以指定View width、height的最小值
/** * 当布局为wrap_content时设置默认长宽 * @param widthMeasureSpec * @param heightMeasureSpec */ @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { setMeasuredDimension(measure(widthMeasureSpec), measure(heightMeasureSpec)); } private int measure(int origin){ int result = DEFAULT_MIN_WIDTH; int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(origin); int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(origin); if(specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){ result = specSize; }else{ if(specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){ result = Math.min(result, specSize); } } return result; }
下面就是最重要的重写onDraw方法来绘制表盘、刻度、指针……,大致流程如下
1、画表盘,用drawCircle绘制一个圆作为表盘, 圆心坐标为(getWidth()/2, getHeight()/2),半径为Math.min(getHeight()/2, getWidth()/2)。
//画外圆 float borderWidth = DEFAULT_BORDER_WIDTH; Paint paintCircle = new Paint(); paintCircle.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); paintCircle.setAntiAlias(true); paintCircle.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth); canvas.drawCircle(getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2, Math.min(getHeight() / 2, getWidth() / 2) - borderWidth / 2, paintCircle);
2、画刻度线,在这里我们可以利用一个`canvas.rotate'方法就可以不用计算角度了
//画刻度线 float degreeLength = 0f; Paint paintDegree = new Paint(); paintDegree.setAntiAlias(true); for(int i=0;i<60;i++){ if(i % 5 == 0){ paintDegree.setStrokeWidth(6); degreeLength = DEFAULT_LONG_DEGREE_LENGTH; }else{ paintDegree.setStrokeWidth(3); degreeLength = DEFAULT_SHORT_DEGREE_LENGTH; } canvas.drawLine(getWidth()/2, Math.abs(getWidth()/2 - getHeight()/2), getWidth()/2, Math.abs(getWidth()/2 - getHeight()/2) + degreeLength, paintDegree); canvas.rotate(360/60, getWidth()/2, getHeight()/2); }
3、画刻度上的数字
//刻度数字 int degressNumberSize = 30; canvas.translate(getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2); Paint paintDegreeNumber = new Paint(); paintDegreeNumber.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER); paintDegreeNumber.setTextSize(degressNumberSize); paintDegreeNumber.setFakeBoldText(true); for(int i=0;i<12;i++){ float[] temp = calculatePoint((i+1)*30, r - DEFAULT_LONG_DEGREE_LENGTH - degressNumberSize/2 - 15); canvas.drawText((i+1)+"", temp[2], temp[3] + degressNumberSize/2-6, paintDegreeNumber); } /** * 根据角度和长度计算线段的起点和终点的坐标 * @param angle * @param length * @return */ private float[] calculatePoint(float angle, float length){ float[] points = new float[4]; if(angle <= 90f){ points[0] = -(float) Math.sin(angle*Math.PI/180) * DEFAULT_POINT_BACK_LENGTH; points[1] = (float) Math.cos(angle*Math.PI/180) * DEFAULT_POINT_BACK_LENGTH; points[2] = (float) Math.sin(angle*Math.PI/180) * length; points[3] = -(float) Math.cos(angle*Math.PI/180) * length; }else if(angle <= 180f){ points[0] = -(float) Math.cos((angle-90)*Math.PI/180) * DEFAULT_POINT_BACK_LENGTH; points[1] = -(float) Math.sin((angle-90)*Math.PI/180) * DEFAULT_POINT_BACK_LENGTH; points[2] = (float) Math.cos((angle-90)*Math.PI/180) * length; points[3] = (float) Math.sin((angle-90)*Math.PI/180) * length; }else if(angle <= 270f){ points[0] = (float) Math.sin((angle-180)*Math.PI/180) * DEFAULT_POINT_BACK_LENGTH; points[1] = -(float) Math.cos((angle-180)*Math.PI/180) * DEFAULT_POINT_BACK_LENGTH; points[2] = -(float) Math.sin((angle-180)*Math.PI/180) * length; points[3] = (float) Math.cos((angle-180)*Math.PI/180) * length; }else if(angle <= 360f){ points[0] = (float) Math.cos((angle-270)*Math.PI/180) * DEFAULT_POINT_BACK_LENGTH; points[1] = (float) Math.sin((angle-270)*Math.PI/180) * DEFAULT_POINT_BACK_LENGTH; points[2] = -(float) Math.cos((angle-270)*Math.PI/180) * length; points[3] = -(float) Math.sin((angle-270)*Math.PI/180) * length; } return points; }
4、画指针
//画指针 Paint paintHour = new Paint(); paintHour.setAntiAlias(true); paintHour.setStrokeWidth(15); Paint paintMinute = new Paint(); paintMinute.setAntiAlias(true); paintMinute.setStrokeWidth(10); Paint paintSecond = new Paint(); paintSecond.setAntiAlias(true); paintSecond.setStrokeWidth(5); Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance(); float[] hourPoints = calculatePoint(now.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY)%12/12f*360, hourPointerLength); canvas.drawLine(hourPoints[0], hourPoints[1], hourPoints[2], hourPoints[3], paintHour); float[] minutePoints = calculatePoint(now.get(Calendar.MINUTE)/60f*360, minutePointerLength); canvas.drawLine(minutePoints[0], minutePoints[1], minutePoints[2], minutePoints[3], paintMinute); float[] secondPoints = calculatePoint(now.get(Calendar.SECOND)/60f*360, secondPointerLength); canvas.drawLine(secondPoints[0], secondPoints[1], secondPoints[2], secondPoints[3], paintSecond);
5、画圆心
//画圆心 Paint paintCenter = new Paint(); paintCenter.setColor(Color.WHITE); canvas.drawCircle(0, 0, 2, paintCenter); 最后只要启动一个无限循环的线程,每隔1秒针重绘一下View就能让指针动起来了 private Thread timeThread = new Thread() { @Override public void run() { try { while(true){ updateHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0); Thread.sleep(1000); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; private Handler updateHandler = new Handler() { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { invalidate(); } };
以上就是教大家如何利用Android画个时钟的详细步骤代码,希望对大家的学习Android软件编程有所帮助。
【Android画个时钟玩玩】相关文章:
